Marjum Formation
Appearance
(Redirected from Marjum Limestone)
| Marjum Formation | |
|---|---|
| Stratigraphic range: Middle Cambrian | |
 Notch Peak Sill intruding into the layers of white marble and grey argillite of the Marjum Formation | |
| Type | Geological formation |
| Overlies | Wheeler Shale |
| Thickness | Up to 430 meters[1] |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | limestone |
| Other | shale, metasedimentary rocks |
| Location | |
| Region | |
| Country | |
| Extent | House Range |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Marjum Pass[2] |
| Named by | Charles D. Walcott |
| Year defined | 1908[2] |
The Marjum Formation is a Cambrian geological formation that overlies the Wheeler Shale in the House Range, Utah.[1][3] It is named after its type locality, Marjum Pass, and was defined in 1908.[2] The formation is known for its occasional preservation of soft-bodied tissue, and is slightly younger than the Burgess Shale,[4] falling in the Ptychagnostus praecurrens trilobite zone.[5]
Fossil content
[edit]Color key
|
Notes Uncertain or tentative taxa are in small text; |
Ambulacrarians
[edit]| Ambulacrarians reported from the Marjum Formation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Material | Notes | Images |
| Castericystis | C. vali | Numerous specimens.[6] | A solutan. |  | |
| Eldonia | E. ludwigi | Marjum Pass (Ptychagnostus punctuosus Zone).[7] | SM X.50204.1 (part) & SM X.50204.2 (counterpart).[7] | A cambroernid. |  |
| Marjumicystis | M. mettae | 7 specimens.[6] | An eocrinoid. | ||
| Mastigograptus | M. sp. | A single specimen.[8] | A mastigograptid graptolite. |  | |
| Totiglobus | T.? lloydi | Locality 811.[9] | 1 specimen (USNM 172047).[9] | An edrioasteroid. | |
Arthropods
[edit]| Arthropods reported from the Marjum Formation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Material | Notes | Images |
| Anomalocaris | A. nathorsti | Sponge Gully.[10] | Partial body (USNM 374593).[10] | Species moved to the genus Peytoia. | |
| Asaphiscus | A. wheeleri | Bathyuriscus fimbriatus Subzone.[11] | A ptychopariid trilobite. |  | |
| Baltagnostus | B. eurypyx | All subzones of the Bolaspidella Zone.[11] | Multiple specimens.[11] | A diplagnostid trilobite. | |
| Bathyuriscidella | B. aff. B. amplicauda | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | 3 pygidia.[11] | A dolichometopid trilobite. | |
| Bathyuriscus | B. elegans | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | Numerous specimens.[11] | A dolichometopid trilobite. | |
| B. fimbriatus | Bathyuriscus fimbriatus & lower Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | Numerous specimens.[11] | A dolichometopid trilobite. |  | |
| Bolaspidella | B. contracta | Bolaspidella contracta & lower Lepojyge calva Subzones.[11] | A menomoniid trilobite. | ||
| B. housensis | Bathyuriscus fimbriatus Subzone.[11] | A menomoniid trilobite. | |||
| B. jarrardi | Localities 347, 391, and 716 (mid-Bolaspidella Zone).[12] | Multiple specimens.[12] | A menomoniid trilobite. | ||
| Branchiocaris | B. pretiosa | Sponge Gully.[10][13] | 3 specimens.[10] | A hymenocarine. |  |
| Buccaspinea | B. cooperi | Kells Knolls locality.[14] | An almost complete specimen (BPM 1108).[14] | A hurdiid, originally reported as Hurdia sp. |  |
| Burlingia | B. halgedahlae | Localities 347 and 716 (mid-Bolaspidella Zone).[12] | Multiple specimens.[12] | A burlingiid trilobite. | |
| Caryosyntrips | C. camurus | 'Red Wash' locality.[14] | 2 isolated frontal appendages.[14] | A panarthropod of uncertain classification. |  |
| Cotalagnostus | C. laevus | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | Over 50 specimens.[11] | A diplagnostid trilobite. | |
| C. sp. | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | A pygidium. | A diplagnostid trilobite. | ||
| Dicranocaris | D. guntherorum | Red Wash, Modocia Flats & Sponge Gully.[13] | 4 specimens.[13] | An arthropod of uncertain classification. | |
| Dytikosicula | D. desmatae | West of Delta, House Range.[7] | 1 specimen (SM X.50203).[7] | A putative megacheiran. | |
| Elrathia | E. alapyge | Bolaspidella contracta & Lejopyge calva Subzones.[11] | Numerous specimens.[11] | A ptychopariid trilobite. | |
| E. marjumi | Bathyuriscus fimbriatus & Bolaspidella contracta Subzones.[11] | Numerous specimens.[11] | A ptychopariid trilobite. | ||
| Emeraldella | E.? sp. | Red Wash.[10] | Part & counterpart (KUMIP 204791).[10] | An artiopod. |  |
| Hemirhodon | H. amplipyge | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | 14 incomplete specimens.[11] | A dolichometopid trilobite. |  |
| Holteria | H. problematica | Marjum Pass (Lejopyge calva Subzone).[11] | A pygidium.[11] | A corynexochid trilobite. | |
| Homagnostus | H. incertus | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | Multiple specimens.[11] | An agnostid trilobite. | |
| Hypagnostus | H. parvifrons | All subzones of the Bolaspidella Assemblage Zone.[11] | Numerous specimens.[11] | A diplagnostid trilobite. |  |
| Itagnostus | I. interstrictus | House Range.[15] | A peronopsid trilobite originally reported as Peronopsis interstricta. |  | |
| Leanchoilia | L.? cf. protogonia | Sponge Gully.[13] | Part & counterpart of a complete specimen (UU 06011.01).[13] | A megacheiran. |  |
| Lejopyge | L. calva | Marjum Pass (Lejopyge calva Subzone).[11] | Numerous specimens.[11] | A ptychagnostid trilobite. | |
| Linguagnostus | L. perplexus | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | Over 20 specimens.[11] | A diplagnostid trilobite. | |
| Marjumia | M. callas | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | A marjumiid trilobite. | ||
| M. typa | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | A marjumiid trilobite. | |||
| Modocia | M. laevinucha | Bathyuriscus fimbriatus & Bolaspidella contracta Subzones.[11] | Many specimens.[11] | A marjumiid trilobite. | |
| M. nuchaspina | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | A marjumiid trilobite. | |||
| M. typicalis | 50 or more specimens.[11] | A marjumiid trilobite. | |||
| Naraoia | N. compacta | Sponge Gully.[16] | 4 specimens.[16] | A naraoiid. |  |
| Neolenus | N. inflatus | East of Antelope Springs.[17] | Multiple specimens & fragments.[17] | A trilobite. | |
| N. intermedius | East of Antelope Springs.[17] | A trilobite. | |||
| N. intermedius pugio | East of Antelope Springs.[17] | 4 specimens of a pygidium.[17] | A trilobite. | ||
| N. superbus | East of Antelope Springs.[17] | Multiple specimens & fragments.[17] | A trilobite. | ||
| Nettapezoura | N. basilika | Sponge Gully.[13] | An arachnomorph. | ||
| Olenoides | O. decorus | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | 7 specimens.[11] | A dorypygid trilobite. | |
| O. inflatus | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | A dorypygid trilobite. |  | ||
| O. marjumensis | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | A dorypygid trilobite. | |||
| O. pugio | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | Numerous specimens.[11] | A dorypygid trilobite. | ||
| O. superbus | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | 7 specimens.[11] | A dorypygid trilobite. |  | |
| Pahvantia | P. hastata | Precise localities unknown.[14] | 3 specimens.[14] | A hurdiid. |  |
| Peronopsis | P. interstricta | House Range.[15] | Numerous specimens.[11] | Reassigned to the genus Itagnostus. | |
| P. segmenta | House Range.[15] | Multiple specimens.[11] | A peronopsid trilobite. | ||
| Perspicaris | P.? ellipsopelta | Ptychagnostus punctuosus Zone.[18] | Valves & carapaces.[18] | A bivalved arthropod. | |
| Peytoia | P. nathorsti | Sponge Gully.[10] | Partial body (USNM 374593) & partial mouthpart (KUMIP 314095).[19] | A hurdiid, formerly named Anomalocaris nathorsti. |  |
| Ptychagnostus | P. akanthodes | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | Numerous specimens.[11] | A ptychagnostid trilobite. | |
| P. atavus | House Range.[15] | A ptychagnostid trilobite. |  | ||
| P. hybridus | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | About 10 specimens.[11] | A ptychagnostid trilobite. | ||
| P. richmondensis | Bathyuriscus fimbriatus Subzone.[11] | Numerous specimens.[11] | A ptychagnostid trilobite. | ||
| P. sp. | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | At least 5 pygidia. | A ptychagnostid trilobite. | ||
| Trymataspis | T. depressa | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | Over 30 specimens.[11] | A lonchocephalid trilobite. | |
| T. lomaleie | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | 10 cranidia.[11] | A lonchocephalid trilobite. | ||
| T. pristina | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | Over 20 cranidia.[11] | A lonchocephalid trilobite. | ||
| Tuzoia | T. guntheri | Ptychagnostus punctuosus Zone.[18] | Multiple valves & carapaces.[18][20] | A hymenocarine. |  |
| Utagnostus | U. trispinulus | Bolaspidella contracta & Lejopyge calva Subzones.[11] | Multiple specimens.[11] | An agnostid trilobite. | |
| Utaspis | U. marjumensis | House Range & Wheeler Amphitheater.[11] | A ptychopariid trilobite. |  | |
| Zacanthoides | Z. sp. | Wheeler Amphitheater (Bolaspidella contracta Subzone).[11] | A cranidium.[11] | A zacanthoidid trilobite. |  |
Chancelloriids
[edit]| Chancelloriids reported from the Marjum Formation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Material | Notes | Images |
| Chancelloria | C. sp. | Bathyuriscus fimbriatus & Bolaspidella contracta Subzones.[11] | About 20 spicules.[11] | A chancelloriid. |  |
Chordates
[edit]| Chordates reported from the Marjum Formation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Material | Notes | Images |
| Megasiphon | M. thylakos | House Range.[21] | One specimen (UMNH.IP.6079).[21] | A tunicate. |  |
| Nuucichthys | N. rhynchocephalus | House range.[22] | One specimen (UMNH.IP.6084)[22] | A basal chordate related to Metaspriggina. |  |
| Skeemella | S. clavula | North of Red Wash (Ptychagnostus punctuosus Biozone).[23] | 2 specimens (KUMIP 314102 & KUMIP 314103).[23] | A vetulicolian. |  |
Cnidarians
[edit]Moon, Caron & Moysiuk (2023) considered these fossils would be ctenophores instead.[24]
| Cnidarians reported from the Marjum Formation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Material | Notes | Images |
| Coronatae? | Indeterminate | Sponge Gully.[25] | 1 specimen (UU07021.05).[25] | A scyphozoan jellyfish, may be referrable to the crown jellyfish family. |  |
| Cubozoa? | Indeterminate | Sponge Gully.[25] | 2 specimens (UU07021.01 & UU07021.02).[25] | Specimens possibly referrable to box jellyfish. |  |
| Narcomedusae? | Indeterminate | Sponge Gully.[25] | 5 specimens (UU07021.03, UU07021.04, UU07021.06, UU07021.07 & UU07021.08).[25] | A hydrozoan tentatively assigned to this family. | 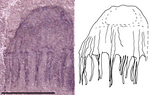 |
| Semaeostomeae? | Indeterminate | Sponge Gully.[25] | 2 specimens (UU07021.09 & UU07021.10).[25] | A scyphozoan jellyfish tentatively assigned to this family. |  |
Ctenophores
[edit]| Ctenophores reported from the Marjum Formation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Material | Notes | Images |
| Ctenorhabdotus | C. campanelliformis | House Range (likely from the lower Ptychagnostus punctuosus Zone).[26] | 1 specimen (UMNH.IP.6125).[26] | A ctenophore. |  |
| Thalassostaphylos | T. elegans | House Range (lower Ptychagnostus punctuosus Zone).[26] | 1 specimen (UMNH.IP.6086).[26] | A ctenophore. | |
Lophotrochozoans
[edit]| Lophotrochozoans reported from the Marjum Formation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Material | Notes | Images |
| Acrothele | A. subsidua | Bathyuriscus-Elrathina & Bolaspidella Zones.[11] | A brachiopod. |  | |
| Helcionella | "H." arguta | Bathyuriscus fimbriatus & Bolaspidella contracta Subzones.[11] | More than 100 specimens.[11] | A helcionellid. | |
| Hyolithes | H. sp. | All subzones of the Bolaspidella Zone.[11] | More than 100 specimens.[11] | A hyolith. |  |
| Lingulella | L. sp. | Bathyuriscus fimbriatus & Bolaspidella contracta Subzones.[11] | An obolid brachiopod. |  | |
| Micromitra | M. modesta | Multiple specimens.[11] | A paterinide brachiopod. |  | |
| Nisusia | N. sulcata | 18 specimens.[27] | A kutorginate brachiopod. |  | |
| Pegmatreta | P. bellatula | Bathyuriscus fimbriatus & Bolaspidella contracta Subzones.[11] | Numerous specimens.[11] | A brachiopod. | |
| P. ophirensis | All subzones of the Bolaspidella Zone.[11] | A brachiopod. | |||
| Pelagiella | P. sp. | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | More than 50 internal molds.[11] | A pelagiellid. |  |
| Prototreta | P. attenuata | Bathyuriscus-Elrathina Zone & Bolaspidella Zone.[11] | A brachiopod. | ||
| P. mimica | Bolaspidella contracta Subzone.[11] | A brachiopod. | |||
| Stenothecoides | S. elongata | Bathyuriscus fimbriatus Subzone.[11] | Over 30 valves.[11] | A stenothecoid. | |
Scalidophorans
[edit]| Scalidophorans reported from the Marjum Formation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Material | Notes | Images |
| Arrakiscolex | A. aasei | Grey Marjum locality (Ptychagnostus punctuosus Zone).[28] | Cuticle fragments.[28] | A palaeoscolecid also known from the Upper Weeks Formation. | |
| Ottoia | O. prolifica | Sponge Gully.[5] | A complete individual (KUMIP 204770).[5] | Referral of the specimen to this species is insecure, better classified as O.? sp.[28][29] | |
| O.? sp. | Sponge Gully.[28] | A complete individual (KUMIP 204770).[28] | A stem-priapulid, specimen formerly referred to Ottoia prolifica or Scathascolex minor.[28] |  | |
| Scathascolex | S. minor | Sponge Gully.[5] | A complete individual (KUMIP 204770).[5][30] | Specimen reassigned to Ottoia? sp.[28] | |
| Selkirkia | S. willoughbyi | Sponge Gully.[5] | Tube with associated soft parts (KUMIP 204788).[5] | A stem-priapulid. |  |
Sponges
[edit]| Sponges reported from the Marjum Formation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Presence | Material | Notes | Images |
| Choia | C. carteri | Sponge Gulch.[31] | A demosponge. |  | |
| C. hindei | Red Cliffs Wash.[31] | 2 specimens & 3 other fragments.[31] | A demosponge. | ||
| C. utahensis | Sponge Gulch.[31] | Several specimens.[31] | A demosponge. | ||
| Diagoniella | D. cyathiformis | Red Cliffs Wash & Kells Knolls Gulch.[31] | Numerous specimens.[31] | A reticulosan. | |
| D. hindei | Sponge Gulch.[31] | Approximately 40 specimens.[31] | A reticulosan. |  | |
| D. magna | Kells Knolls Gulch (Bathyuriscus fimbriatus zone).[32] | A fragment (USNM 535922).[32] | A reticulosan. | ||
| D. sp. | Sponge Gulch.[31] | 2 large fragments.[31] | A reticulosan. | ||
| Hamptonia | H. bowerbanki | Red Cliffs Wash & Sponge Gulch.[31] | Multiple specimens.[31] | A demosponge. | |
| Hazelia | H. palmata | Near Marjum Pass.[33] | One specimen.[33] | A demosponge. |  |
| Hintzespongia | H. bilamina | Kells Knolls Gulch (Bathyuriscus fimbriatus zone).[31][32] | Multiple specimens.[31][32] | A reticulosan. | |
| Hexactinellida | Indeterminate | Miscellaneous spicules.[11] | Indeterminate glass sponges, originally reported as Hyalospongiae (now a junior synonym). | ||
| Kiwetinokia | Drum Mountains.[31] | 4 large slabs.[31] | A reticulosan. | ||
| Leptomitus | L. metta | Red Cliffs Wash locality.[31] | 22 specimens.[31] | A demosponge. | |
| Polygoniella | P. turrelli | House Range[34] | Around 200 specimens[34] | A glass sponge |  |
| Protospongia | P.? elongata | Sponge Gulch.[31] | 1 specimen.[31] | A reticulosan. | |
| Testiispongia | T. venula | Sponge Gulch.[31] | Several specimens.[31] | A glass sponge. | |
| Valospongia | V. gigantis | Sponge Gulch.[31] | A reticulosan. | ||
| V.? gigantus | Kells Knolls Gulch (Bathyuriscus fimbriatus zone).[32] | A fragment (USNM 535917).[32] | A reticulosan. | ||
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Foster, John; Gaines, Robert (October 2016). "Taphonomy and paleoecology of the "middle" Cambrian (Series 3) formations in Utah's West Desert: Recent finds and new data". Utah Geological Association Publication. 45: 291–336.
- ^ a b c Walcott, Charles D. (1910). "Nomenclature of some cambrian cordilleran formations". Smithsonian Miscellaneous Collections. 53 (1): 1–12. hdl:10088/23377.
- ^ "Trilobites of The Marjum Formation".
- ^ Robison, R. A. (1964). "Upper Middle Cambrian Stratigraphy of Western Utah". Geological Society of America Bulletin. 75 (10): 995–1010. Bibcode:1964GSAB...75..995R. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1964)75[995:UMCSOW]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0016-7606.
- ^ a b c d e f g Conway Morris, S.; Robison, R. A. (1986). "Middle Cambrian priapulids and other soft-bodied fossils from Utah and Spain". University of Kansas Paleontological Contributions. 117: 1–22. hdl:1808/3696.
- ^ a b Ubaghs, G.; Robison, Richard A. (September 1985). "A homoiostelean and a new eocrinoid from the Middle Cambrian of Utah". University of Kansas Paleontological Contributions (115): 1–24.
- ^ a b c d Conway Morris, Simon; Selden, Paul A.; Gunther, Glade; Jamison, Paul G.; Robison, Richard A. (May 2015). "New records of Burgess Shale-type taxa from the middle Cambrian of Utah". Journal of Paleontology. 89 (3): 411–423. Bibcode:2015JPal...89..411C. doi:10.1017/jpa.2015.26. ISSN 0022-3360.
- ^ LoDuca, Steven T.; Kramer, Anthony (March 2014). "Graptolites from the Wheeler and Marjum Formations (Cambrian, Series 3) of Utah". Journal of Paleontology. 88 (2): 403–410. Bibcode:2014JPal...88..403L. doi:10.1666/12-096. ISSN 0022-3360. S2CID 140553697.
- ^ a b Sprinkle, James (January 1985). "New edrioasteroid from the Middle Cambrian of western Utah". University of Kansas Paleontological Contributions. 116: 1–4.
- ^ a b c d e f g Briggs, D. E. G.; Robison, Richard A. (January 1984). "Exceptionally preserved nontrilobite arthropods and Anomalocaris from the Middle Cambrian of Utah". University of Kansas Paleontological Contributions. 111: 1–23.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce Robison, Richard A. (1964). "Late Middle Cambrian Faunas from Western Utah". Journal of Paleontology. 38 (3): 510–566. ISSN 0022-3360. JSTOR 1301528.
- ^ a b c d Robison, Richard A.; Babcock, Loren E. (2011-11-30). "Systematics, paleobiology, and taphonomy of some exceptionally preserved trilobites from Cambrian Lagerstätten of Utah". Paleontological Contributions (5): 1–47. doi:10.17161/PC.1808.8543. ISSN 1946-0279.
- ^ a b c d e f Briggs, Derek E. G.; Lieberman, Bruce S.; Hendricks, Jonathan R.; Halgedahl, Susan L.; Jarrard, Richard D. (2008). "Middle Cambrian arthropods from Utah". Journal of Paleontology. 82 (2): 238. Bibcode:2008JPal...82..238B. doi:10.1666/06-086.1. ISSN 0022-3360. S2CID 31568651.
- ^ a b c d e f Pates, Stephen; Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Daley, Allison C.; Kier, Carlo; Bonino, Enrico; Ortega-Hernández, Javier (2021-01-19). "The diverse radiodont fauna from the Marjum Formation of Utah, USA (Cambrian: Drumian)". PeerJ. 9: e10509. doi:10.7717/peerj.10509. ISSN 2167-8359. PMC 7821760. PMID 33552709.
- ^ a b c d Robison, R. A. (1982). "Some Middle Cambrian Agnostoid Trilobites from Western North America". Journal of Paleontology. 56 (1): 132–160. ISSN 0022-3360. JSTOR 1304500.
- ^ a b Robison, Richard A. (1984-07-24). "New Occurrences of the Unusual Trilobite Naraoia From the Cambrian of Idaho and Utah". University of Kansas Paleontological Contributions. 112: 1–8.
- ^ a b c d e f g Walcott, Charles D. (1908-04-25). "Cambrian Trilobites". Smithsonian Miscellaneous Collections. 53 (2): 14–52. hdl:10088/23376.
- ^ a b c d Robison, Richard A.; Richards, B. C. (1981-12-16). "Large bivalve arthropods from the Middle Cambrian of Utah". University of Kansas Paleontological Contributions. 106: 1–19.
- ^ Pates, Stephen; Daley, Allison C.; Lieberman, Bruce S. (January 2018). "Hurdiid radiodontans from the middle Cambrian (Series 3) of Utah". Journal of Paleontology. 92 (1): 99–113. Bibcode:2018JPal...92...99P. doi:10.1017/jpa.2017.11. ISSN 0022-3360. S2CID 135388079.
- ^ Vannier, Jean; Caron, Jean-Bernard; Yuan, Jin-Liang; Briggs, Derek E. G.; Collins, Desmond; Zhao, Yuan-Long; Zhu, Mao-Yan (May 2007). "Tuzoia: Morphology and Lifestyle of a Large Bivaled Arthropod of the Cambrian Seas". Journal of Paleontology. 81 (3): 445–471. Bibcode:2007JPal...81..445V. doi:10.1666/pleo05070.1. ISSN 0022-3360. S2CID 197540482.
- ^ a b Nanglu, Karma; Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Weaver, James C.; Ortega-Hernández, Javier (2023-07-06). "A mid-Cambrian tunicate and the deep origin of the ascidiacean body plan". Nature Communications. 14 (1): 3832. Bibcode:2023NatCo..14.3832N. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-39012-4. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 10325964. PMID 37414759.
- ^ a b Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Ortega-Hernández, Javier (2024-07-24). "A long-headed Cambrian soft-bodied vertebrate from the American Great Basin region". Royal Society Open Science. 11 (7). Bibcode:2024RSOS...1140350L. doi:10.1098/rsos.240350. ISSN 2054-5703. PMC 11267725. PMID 39050723.
- ^ a b Kimmig, Julien; Leibach, Wade W.; Lieberman, Bruce S. (2020-05-30). "First occurrence of the problematic vetulicolian Skeemella clavula in the Cambrian Marjum Formation of Utah, USA". Carnets de géologie (Notebooks on geology). 20 (10): 215–221. doi:10.4267/2042/70836. hdl:1808/33460. S2CID 219178949.
- ^ Moon, Justin; Caron, Jean-Bernard; Moysiuk, Joseph (2023-08-09). "A macroscopic free-swimming medusa from the middle Cambrian Burgess Shale". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 290 (2004). doi:10.1098/rspb.2022.2490. ISSN 0962-8452. PMC 10394413. PMID 37528711.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Cartwright, Paulyn; Halgedahl, Susan L.; Hendricks, Jonathan R.; Jarrard, Richard D.; Marques, Antonio C.; Collins, Allen G.; Lieberman, Bruce S. (2007-10-31). Humphries, Stuart (ed.). "Exceptionally Preserved Jellyfishes from the Middle Cambrian". PLOS ONE. 2 (10): e1121. Bibcode:2007PLoSO...2.1121C. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001121. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 2040521. PMID 17971881.
- ^ a b c d Parry, Luke A.; Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Weaver, James C.; Ortega-Hernández, Javier (2021-09-24). "Cambrian comb jellies from Utah illuminate the early evolution of nervous and sensory systems in ctenophores". iScience. 24 (9): 102943. Bibcode:2021iSci...24j2943P. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2021.102943. ISSN 2589-0042. PMC 8426560. PMID 34522849.
- ^ Holmer, Lars E.; Popov, Leonid E.; Ghobadi Pour, Mansoureh; Claybourn, Tom; Zhang, Zhiliang; Brock, Glenn A.; Zhang, Zhifei (2018-01-09). "Evolutionary significance of a middle Cambrian (Series 3) in situ occurrence of the pedunculate rhynchonelliform brachiopod Nisusia sulcata". Lethaia. 51 (3): 424–432. Bibcode:2018Letha..51..424H. doi:10.1111/let.12254. ISSN 0024-1164.
- ^ a b c d e f g Leibach, Wade; Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Whitaker, Anna; Schiffbauer, James; Kimmig, Julien (September 2021). "First palaeoscolecid from the Cambrian (Miaolingian, Drumian) Marjum Formation of western Utah". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 66. doi:10.4202/app.00875.2021.
- ^ Smith, Martin R.; Harvey, Thomas H. P.; Butterfield, Nicholas J. (May 2015). Kouchinsky, Artem (ed.). "The macro- and microfossil record of the Cambrian priapulid Ottoia". Palaeontology. 58 (4): 705–721. Bibcode:2015Palgy..58..705S. doi:10.1111/pala.12168. ISSN 0031-0239.
- ^ Smith, Martin R. (2015-10-15). Sigwart, Julia (ed.). "A palaeoscolecid worm from the Burgess Shale". Palaeontology. 58 (6): 973–979. Bibcode:2015Palgy..58..973S. doi:10.1111/pala.12210.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x Rigby, J. Keith (1983). "Sponges of the Middle Cambrian Marjum Limestone from the House Range and Drum Mountains of Western Millard County, Utah". Journal of Paleontology. 57 (2): 240–270. ISSN 0022-3360. JSTOR 1304651.
- ^ a b c d e f Rigby, J. Keith; Church, Stephen B.; Anderson, Nicolle K. (2010). "Middle Cambrian Sponges from the Drum Mountains and House Range in Western Utah". Journal of Paleontology. 84 (1): 66–78. Bibcode:2010JPal...84...66R. doi:10.1666/08-046.1. ISSN 0022-3360. JSTOR 20627693. S2CID 130205628.
- ^ a b Rigby, J. Keith; Gunther, Lloyd F.; Gunther, Freida (November 1997). "The first occurrence of the Burgess Shale demosponge Hazelia palmata Walcott, 1920, in the Cambrian of Utah". Journal of Paleontology. 71 (6): 994–997. Bibcode:1997JPal...71..994R. doi:10.1017/S0022336000035976. ISSN 0022-3360. S2CID 130706440.
- ^ a b Del Mouro, Lucas; Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Botting, Joseph; Coleman, Robert; Gaines, Robert R.; Skabelund, Jacob; Weaver, James C.; Ortega-Hernández, Javier (2024-09-18). "A new sponge from the Marjum Formation of Utah documents the Cambrian origin of the hexactinellid body plan". Royal Society Open Science. 11 (9). doi:10.1098/rsos.231845. ISSN 2054-5703. PMC 11407857. PMID 39295920.
